Heartburn is a common condition that is characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat. It is caused by the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus.
What Is Heartburn
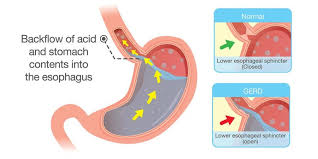
Heartburn is a common condition that is characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat. It is caused by the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus. When the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscle that separates the esophagus and stomach, relaxes or weakens, the acid can flow back into the esophagus and cause irritation. This can lead to symptoms such as a burning sensation in the chest (often behind the breastbone), a sour taste in the mouth, and difficulty swallowing.
Risk factors for heartburn include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, and consuming certain foods and beverages that can relax the LES and increase acid production in the stomach such as chocolate, coffee, alcohol, acidic fruits, and tomato-based products.
This health condition can often be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications such as antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These medications neutralize or reduce the amount of acid in the stomach to relieve symptoms. Avoiding foods and drinks that trigger heartburn, eating smaller meals, and not eating close to bedtime can also help prevent heartburn.
If this persists or becomes severe, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider, as it may be a symptom of a more serious condition such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or Barrett’s esophagus.
Causes Of Heartburn
Causes can be broadly categorized as follows:
Gastrointestinal causes:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Hiatal hernia
- Gastroparesis
- Esophagitis
- Barrett’s esophagus
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
It is the most common gastrointestinal cause of heartburn. It occurs when the muscle that separates the stomach and esophagus (the lower esophageal sphincter) does not function properly, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. This can cause irritation and inflammation, leading to heartburn and other symptoms.
Hiatal hernia:
It is another common gastrointestinal cause of heartburn. It occurs when part of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm and into the chest. This can put pressure on the stomach and cause acid reflux.
Gastroparesis:
It is a condition where the stomach muscles are not able to properly contract and push food out of the stomach. This can cause food to stay in the stomach for too long and cause acid reflux.
Esophagitis:
It is an inflammation of the esophagus caused by acid reflux.
Barrett’s esophagus:
It is a condition where the cells in the esophagus change, becoming more like the cells in the stomach or small intestine. This is caused by long-term acid reflux and can increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
Lifestyle and dietary causes:
- Eating large meals
- Eating close to bedtime
- Consuming certain foods and drinks, such as chocolate, tomatoes, citrus fruits, peppermint, and carbonated beverages
- Consuming certain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), aspirin, and certain antibiotics
- Stress
- Smoking
- Obesity
Eating large meals or eating close to bedtime can cause heartburn as the stomach is full and the acid has a greater chance of flowing back into the esophagus.
Certain foods and drinks can also trigger heartburn, such as spicy or fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, tomatoes, citrus fruits, and peppermint.
Smoking can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter and increase acid production in the stomach, leading to this condition.
Obesity can put pressure on the stomach and cause acid reflux.
Stress can also increase the risk of heartburn.
Medical conditions:
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
- Scleroderma
- Asthma
- Thyroid diseases
Pregnancy can cause heartburn as the growing uterus puts pressure on the stomach.
Some medical conditions such as diabetes and scleroderma can also cause heartburn. Asthma can cause heartburn as the acid reflux can aggravate asthma symptoms, and some medications used to treat asthma can also cause heartburn as a side effect.
Certain thyroid disorders can also cause heartburn as they affect the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms Of Heartburn
The most common symptom of heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest, often behind the breastbone or in the middle of the chest. This burning sensation can sometimes extend up into the throat.
Other symptoms may include:
- A bitter or sour taste in the mouth
- Pain or discomfort in the chest, particularly after eating or lying down
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness or sore throat
- Dry cough
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Bloating or belching
In some cases, this condition may be mistaken for a heart attack, so it’s important to be aware of the differences in symptoms and seek medical attention if you experience chest pain or pressure that is severe or lasts longer than a few minutes.
It’s important to note that this condition can be caused by a variety of factors and the symptoms may vary from person to person. If you have persistent or severe heartburn, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
How To Get Rid Of Heartburn
There are several ways to get rid of heartburn:
Lifestyle changes:
- Avoiding certain foods and drinks that trigger heartburn, such as spicy or fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, tomatoes, citrus fruits, and peppermint.
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals rather than large meals.
- Waiting at least 3 hours after eating before lying down or going to bed.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing to avoid putting pressure on the stomach.
- Avoiding smoking and alcohol
- Losing weight if you are overweight or obese
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation
Medications:
- Over-the-counter antacids, such as Tums or Rolaids, can neutralize stomach acid and provide quick relief.
- H2 receptor antagonists, such as famotidine (Pepcid) and cimetidine (Tagamet), can reduce the production of stomach acid and provide relief for up to 12 hours.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole (Prilosec), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and esomeprazole (Nexium), can reduce the production of stomach acid and provide relief for up to 24 hours.
3. Prescription Medications:
– Prokinetics can help empty the stomach faster and prevent reflux
– Prost
Home Remedies To Treat Heartburn
There are several home remedies that may help to relieve heartburn:
Baking soda For Heartburn:
Mixing a teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of water can help neutralize stomach acid and provide quick relief. However, it’s important to note that baking soda is high in sodium, so it should be used in moderation and avoided by those with high blood pressure or other conditions that require a low-sodium diet.
Ginger For Heartburn:
Ginger has natural anti-inflammatory properties and can help to reduce inflammation in the esophagus. Drinking ginger tea or taking a ginger supplement may provide relief from burning.
Chewing gum For Heartburn:
Chewing gum can help to stimulate the production of saliva, which can neutralize stomach acid. It may also help to clear acid from the esophagus by promoting the swallowing of saliva.
Apple Cider Vinegar For Heartburn:
Mixing one or two tablespoons of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water and drinking it before meals may help reduce heartburn symptoms.
Aloe vera juice For Heartburn:
Aloe vera juice may help to reduce inflammation in the esophagus and stomach, providing relief from heartburn.
Dgl (Deglycyrrhizinated licorice) For Heartburn:
Dgl is a licorice extract that is thought to have anti-inflammatory properties and can help to soothe the lining of the esophagus.
It’s important to note that these remedies may not work for everyone and some may have side effects. If you have persistent or severe heartburn, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
What are the complications associated with heartburn?
Chronic heartburn, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can lead to several complications if left untreated.
Some of the complications associated with heartburn include:
Esophagitis:
This is inflammation of the lining of the esophagus caused by stomach acid exposure. It can lead to symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, pain, and bleeding.
Barrett’s esophagus:
This is a condition in which the cells in the lining of the esophagus change, becoming abnormal. It increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
Esophageal strictures:
Chronic acid reflux can cause the esophagus to narrow, making it difficult to swallow food.
Chronic cough:
Stomach acid that flows back into the lungs can cause a chronic cough and other respiratory symptoms.
Laryngitis:
Stomach acid can irritate the vocal cords, leading to hoarseness and other voice problems.
Tooth erosion:
Stomach acid can erode tooth enamel, leading to tooth decay and other dental problems.
Asthma:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may cause or worsen asthma symptoms.
Sleep apnea:
GERD can cause people to wake up frequently throughout the night, leading to poor sleep and daytime fatigue.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you have persistent or severe heartburn symptoms, as these complications can be prevented or treated when caught early.
Conclusion
heartburn is a common condition characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat. It is caused by acid reflux, which occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.
There are several factors that can contribute to heartburn, including gastrointestinal issues such as GERD and hiatal hernia, lifestyle and dietary habits, certain medical conditions, and certain medications.
Symptoms may include burning sensations in the chest, a bitter or sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and a dry cough.
To get rid of heartburn, there are several strategies that can be employed including making lifestyle changes, using over-the-counter and prescription medications, and trying home remedies such as ginger, baking soda, apple cider vinegar, aloe vera juice, and Dgl. If you have persistent or severe heartburn, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.