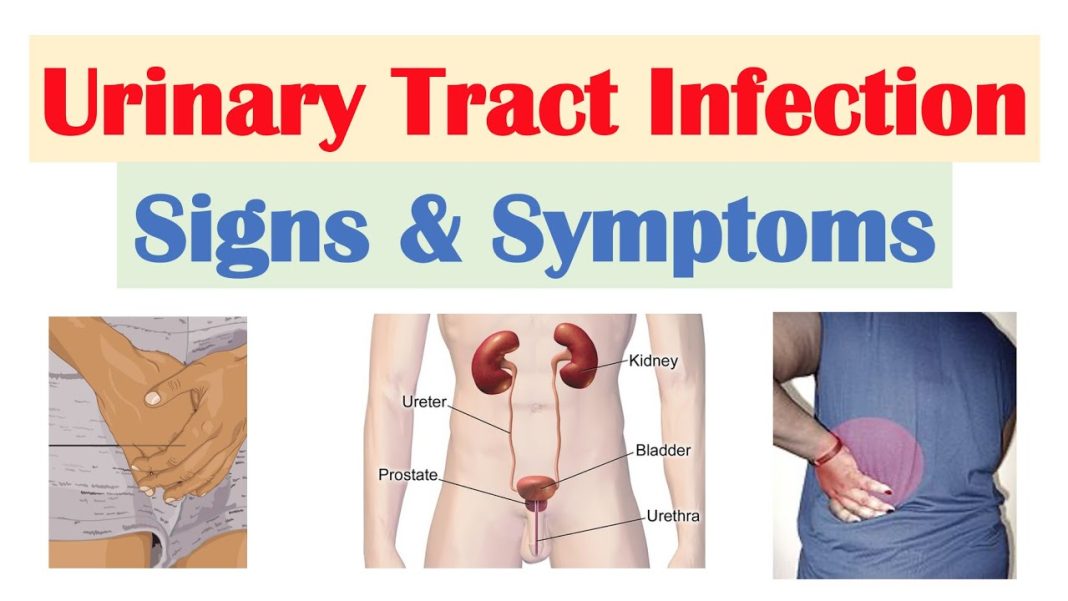
Urine infection is an infection in any part of the urinary system including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Do you know urine infection affects about 60% of women and 12% of men during their lifetime? Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than men because women have shorter urethras than men so bacteria have fewer distances to travel to reach the bladder. Read this post till the end to find out the types, causes, symptoms, and prevention of urine infection.
Although urine infection is very common, it is important to consult a doctor if you think you may have a urine infection. Early treatment of urinary infections can help to prevent infection from spreading to the bladder or kidneys. Your doctor will check which micro-organism is present in your urine. Urinary tract infections usually respond quickly and well to antibiotics.
Causes Of Urine Infection (UTI)
Bacteria normally do not live in the urinary tract that lives around the vagina and rectum. When bacteria get into the urine from the urethra and travel into the bladder, they cause Urine infection.
Sexual intercourse may move bacteria into the urinary tract. This happens most in some women.
The most common germ-causing urinary tract infection is found in the digestive system, Escherichia coli (E.coli). It can easily spread to the urethra and stick to the lining of your urinary system.
Risk Factors For Developing UTI
Urine Infection In Women
Urine infections are more common in women than men because women have shorter urethras than women so bacteria have fewer distances to travel to reach the bladder.
Risk factors that are specific to women include:
· Menopause:
The protection that estrogen proves against urine infection and the lining of the vagina begins to change during menopause. These changes increase the risk of urine infection.
· Birth control:
Using diaphragms for birth control may increase the risk of urine infection.
· Female anatomy:
Urine infections are more common in women than men because women have shorter urethras than women so bacteria have fewer distances to travel to reach the bladder.
Urine Infection In Men:
Men can get UTIs, particularly if they have trouble with urine flow. If the bladder is not emptying properly, the buildup of urine makes it more difficult to cure the infection.
Urine Infection In Babies:
Urine infections in babies always need to be investigated as they may indicate a serious underlying condition, called urinary reflux. This allows urine to flow back into the kidneys from the bladder. Reflux increases the risk of infection as it causes the urine to stay inside the body.
Diabetes:
People with diabetes (high blood sugar) are at increased risk of having UTIs as their urine may have a higher content of glucose (sugar). High glucose level makes it easier for bacteria to multiply. Diabetes may also change the body’s immune system making it harder to fight a UTI.
Catheter Use:
People who can’t urinate on their own often must use a tube, called a catheter, to urinate. Using a catheter increases the risk of UTIs. They may also be used by people who have neurological problems that make it difficult to control urination or who are paralyzed.
Blockages In The Urinary Tract:
Kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can trap urine in the bladder. This causes infection to occur.
Urine Infection Symptoms
Symptoms of a UTI depend on what part of the urinary tract is infected.
Types Of Urine Infection
There are different types of urine infections. The type of infection depends on which part of the urine tract is infected.
The different types of UTIs can include:
1. Cystitis:
It is the most common lower urinary tract infection. It is a bacterial infection that has moved up from the urethra.
Symptoms Of Cystic:
- Pelvic pressure
- Lower belly discomfort
- Frequent, painful urination
- Blood in urine
2. Urethritis:
It is the infection of the urethra. Bacteria that infect only the urethra (the short tube that delivers pee from the bladder to the outside of the body).
Symptoms Of Urethritis:
- Burning with urination
- Discharge
3. Pyelonephritis:
Infection of the kidneys. Bacteria enter the body through the urethra and begin to multiply and spread up to the bladder. In this type one or both kidneys can become infected by bacteria or viruses. From there, the bacteria travel through the ureters to the kidneys.
Symptoms Of Pyelonephritis:
- Back or side pain
- High fever
- Cloudy urine
- Urgent or frequent urination
- Fishy smelling urine
- Shaking and chills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
4. Vaginitis:
Infection of the vagina. Bacteria, yeast, viruses, chemicals in creams or sprays, and even clothing can cause vaginitis.
Symptoms Of Vaginitis:
- Vaginal itching and burning.
- Vaginal soreness and redness.
- A change in the color and amount of vaginal discharge.
- Inflamed or swollen skin around the vagina and vulva
- Pelvic pain
- Painful urination.
Complication Of Urine Infection:
When urine infection is left untreated it causes serious health problems:
- Kidney infection due to untreated urine infection damages the kidney permanently.
- Delivering a low birth weight or premature infant when a UTI occurs during pregnancy.
- A narrowed urethra in men from having repeated infections of the urethra.
- Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening complication of an infection. This is a risk especially if the infection travels up the urinary tract to the kidneys.
Prevention:
1. Plenty Of Water:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day. This leads to urine more often and allows bacteria to be flushed out from the urinary tract before the infection begins.
2. Empty Bladder:
Empty your bladder frequently allows bacteria to be flushed out before the infection begins. Drink lots of water, it will be tough to go too long without urinating if you are well-hydrated.
3. Change Birth Control Method:
Diaphragms, unlubricated condoms, or condoms treated with spermicide can contribute to bacterial growth.
4. Cranberry:
Cranberries work by helping to prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract. Take cranberry juice or you can take cranberry supplements daily to treat urine infection at home.
5. Avoid Holding Urine:
Holding urine can weaken the bladder muscles over time. Avoid holding urine for long periods of time because of this causes urinary tract infections due to bacteria build-up.
6. Wipe Yourself:
Wiping yourself after a bowel movement and urinating can also help to prevent infection. It helps prevent the spread of bacteria from the anus to the vagina and urethra.
7. Avoid irritating feminine products:
Using irritating feminine products in the genital area can irritate the urethra. These products include deodorant sprays, douches and powders, intimate washes, and other types of vaginal cleansers were linked with a higher risk of urine infections.
8. Avoid Constipation:
If you are frequently constipated, you may be at greater risk of a UTI. It is difficult to empty your bladder all the way when you are constipated. This leads to bacteria trapped in your bladder for more time to grow and cause infection.
Conclusion:
It is important to consult a doctor if you think you may have a urine infection. Early treatment of urinary infections can help to prevent infection from spreading to the bladder or kidneys. If these infections are left untreated, they could damage the kidneys or spread to the bloodstream.