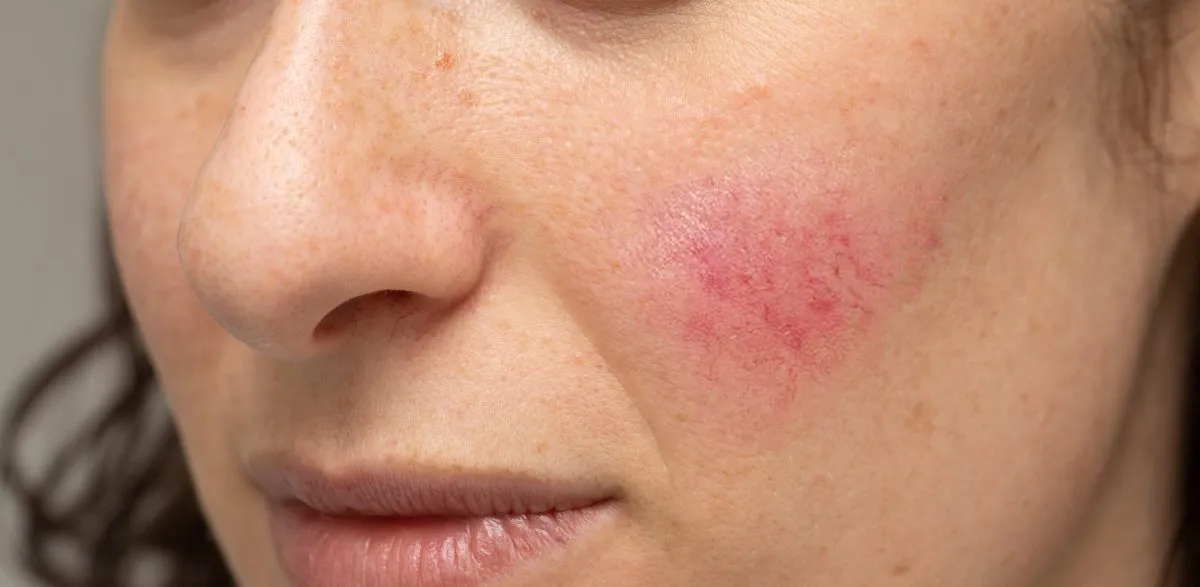
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness and inflammation on the face, especially on the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. Scroll till the end to learn the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of Rosacea.
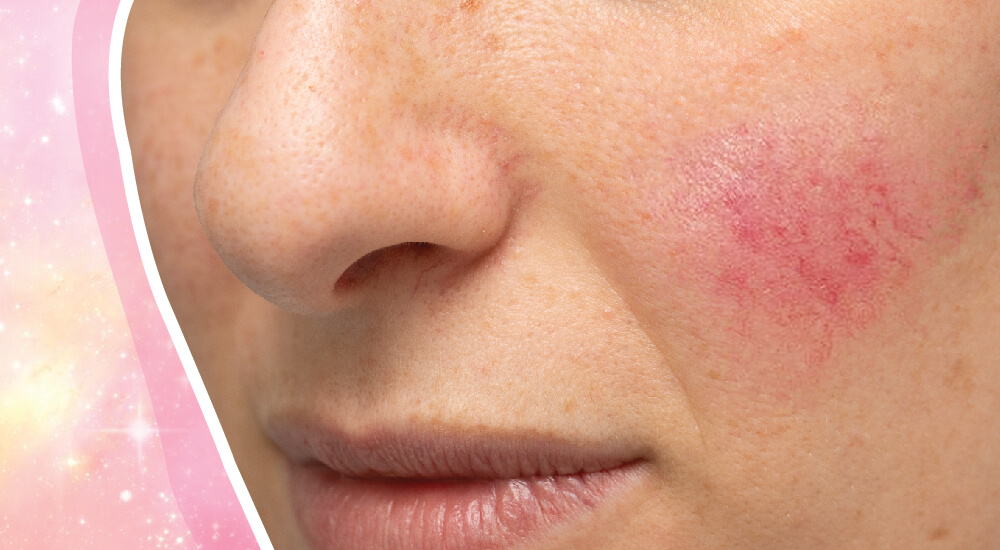
Rosacea is not contagious or life-threatening, but it can be embarrassing and can negatively impact a person’s quality of life. There is no cure for rosacea, but it can be managed with a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Home treatments such as keeping the skin clean, avoiding triggers, using sunscreen, and applying moisturizer may help reduce symptoms. Topical creams and oral antibiotics can also be prescribed by a healthcare provider to help control inflammation and redness.
It’s important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the condition from getting worse.
What Is Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness and inflammation on the face, especially on the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. It may also cause small, red, pus-filled bumps and can make blood vessels more visible. The exact cause of rosacea is not known, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is often characterized by flare-ups and remissions and is more common in people with fair skin, especially those of Celtic or Scandinavian descent.
Rosacea Causes:
The exact cause of rosacea is not known, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential causes or triggers of rosacea include:
- Abnormalities in the blood vessels of the face
- An overgrowth of a certain type of bacteria on the skin
- An immune system reacts to certain factors, such as mites that live on the skin
- Hormonal changes
- Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or vasodilators
- Exposure to sunlight or other sources of UV radiation
- Exposure to hot or cold temperatures
- Exposure to wind or other harsh environmental conditions
- Certain types of food and beverages, such as spicy foods, alcohol, and hot drinks
- Emotional stress
It is important to note that different people may have different triggers for their rosacea, and what triggers one person’s rosacea may not affect another person.
Rosacea Symptoms:
The symptoms of rosacea vary from person to person, but common symptoms include redness, small, red, pus-filled bumps, and visible blood vessels in the face. Some people may also experience dryness, itching, and burning sensations in the affected area. Some people may also experience eye irritation and swollen, red skin on the nose and cheeks. In severe cases, the nose may become enlarged and bumpy from excess tissue.
Additional symptoms of rosacea may include:
Flushing:
This is a temporary redness that occurs on the face, usually in response to triggers such as heat, cold, stress, or alcohol consumption.
Persistent redness:
This occurs when the redness does not go away and is a constant feature of the condition.
Papules and Pustules:
These are small, red, pus-filled bumps that can appear on the face. They may be tender to the touch.
Telangiectasia:
This is the appearance of small, dilated blood vessels on the face, which can be visible through the skin. They are often described as spider veins or thread veins.
Rhinophyma:
This is a condition that can develop in men, where the nose becomes enlarged and bumpy due to excess tissue.
Eye irritation and dryness:
Some people with rosacea may experience eye irritation, dryness, and even vision problems.
Burning and stinging sensation:
Some people may experience a burning or stinging sensation on the affected skin.
Swelling:
The skin may become swollen, especially around the eyes and cheeks.
It’s important to note that the severity of these symptoms can vary from person to person. Some people may experience only a few mild symptoms, while others may have severe symptoms that affect their daily life. Additionally, the symptoms can come and go in cycles and may be triggered by various factors such as stress, spicy food, alcohol, and exposure to the sun.
Rosacea Treatment:
Treatment for rosacea is typically aimed at reducing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. The type of treatment that is best for you will depend on the severity of your symptoms and the extent of your condition. Some common treatments for rosacea include:
Topical medications For Rosacea:
These are creams or gels that are applied directly to the skin. They can help to reduce redness, inflammation, and the number of papules and pustules. Examples include metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin.
Oral medications For Rosacea:
These are medications that are taken by mouth. There are several oral medications that can be used to treat rosacea. These include:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics, such as tetracyclines (doxycycline and minocycline), macrolides (erythromycin), and metronidazole, can help reduce inflammation and redness associated with rosacea.
- Isotretinoin: This medication is used to treat severe cases of rosacea that do not respond to other treatments. Isotretinoin can help reduce the number of bumps and pimples and improve the overall appearance of the skin.
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs like cyclosporine and azathioprine are used to suppress the immune system, they can help reduce inflammation and redness associated with rosacea.
It’s important to note that oral medications should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider and after a proper diagnosis. Some of these medications can cause side effects and may not be suitable for everyone. It’s also important to follow the recommended dosage and duration of treatment to avoid complications.
It’s also important to note that oral medications should be used in conjunction with other therapies such as lifestyle changes and topical treatments to achieve optimal results.
Treatment Of Rosacea At Home
In addition to the treatment options I previously mentioned, there are also some lifestyle changes and self-care measures you can take to help manage rosacea and reduce flare-ups:
Moisturize:
Keeping your skin moisturized can help to reduce dryness, itching, and burning. Use a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer that is appropriate for your skin type. You can use fresh aloe vera gel or raw honey to moisturize your skin.
Avoid extreme temperatures:
Try to avoid sudden changes in temperature, such as hot showers or saunas, as these can aggravate rosacea.
Avoid rubbing or touching your face:
Rubbing or touching your face can irritate the skin and cause flare-ups.
Use makeup carefully:
Choose makeup that is non-comedogenic and hypoallergenic, and avoid using heavy foundation.
Take care of your eyes:
If your rosacea affects your eyes, use artificial tears to lubricate your eyes and avoid wearing contact lenses.
Keep a journal:
Keeping track of your symptoms and triggers can help you to identify patterns and take steps to avoid flare-ups.
Keeping your skin clean:
Gently wash your face with mild soap and lukewarm water, and avoid scrubbing or using hot water.
Avoiding triggers:
Identify and avoid things that cause your rosacea to flare up, such as certain foods, alcohol, and exposure to sun or wind.
Using sunscreen:
Sun exposure can make rosacea worse, so use sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day.
Using over-the-counter creams:
Topical creams containing metronidazole or azelaic acid may help reduce redness and inflammation.
Avoid certain skincare products:
Avoid using products that contain alcohol, witch hazel, or menthol, as they can irritate the skin.
It’s also important to consult with a dermatologist or other healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns about your rosacea. They can provide additional guidance and support and can help you to manage your condition effectively.
It’s also important to note that, even with treatment, rosacea is a chronic condition, which means that it may not go away completely. However, with the right treatment and self-care measures, you can manage your symptoms and reduce the number of flare-ups.
Rosacea Prevention:
Preventing rosacea can be challenging, as the exact cause of the condition is not yet known, and triggers can vary from person to person. However, there are a few steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing rosacea or to prevent flare-ups if you already have the condition:
Identify your triggers:
Keep a journal of your symptoms, and try to identify any common factors that seem to trigger flare-ups. Common triggers include sun exposure, stress, alcohol, spicy foods, and hot drinks. Once you have identified your triggers, try to avoid them as much as possible.
Protect your skin from the sun:
Sun exposure can aggravate rosacea, so it’s important to protect your skin from the sun. Use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and wear a wide-brimmed hat to protect your face.
Avoid hot drinks and spicy foods:
Hot drinks and spicy foods can cause flushing, which can aggravate rosacea. Try to avoid these foods and drinks as much as possible.
Avoid harsh skincare products:
Harsh skincare products can irritate the skin and cause flare-ups. Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products and avoid exfoliating products.
Avoid extreme temperatures:
Exposure to extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can cause flushing and aggravate rosacea. Try to avoid sudden temperature changes and extreme temperatures.
Manage stress:
Stress can be a trigger for rosacea, so try to manage stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or exercise.
It’s also important to see a dermatologist if you suspect you have rosacea, as they can help you to manage the condition through treatments such as topical creams, oral antibiotics, and laser therapy.
Conclusion:
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels on the face. It can also cause bumps or pimples, and in some cases, thickened skin or eye irritation. The exact cause of rosacea is not known, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
There is no cure for rosacea, but it can be managed with a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Home treatments such as keeping the skin clean, avoiding triggers, using sunscreen, and applying moisturizer may help reduce symptoms. Topical creams and oral antibiotics can also be prescribed by a healthcare provider to help control inflammation and redness.
It’s important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the condition from getting worse.