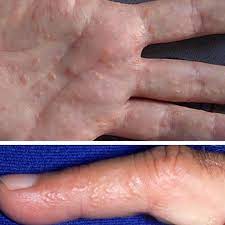
Dyshidrotic eczema is a type of eczema that affects the skin on the hands and feet. Treatment options include the use of topical and oral medications, as well as light therapy. Scroll till the end to find out the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of Dyshidrotic eczema. On this platform, you’ll also learn some effective home remedies for Dyshidrotic eczema that helps to treat this condition naturally.
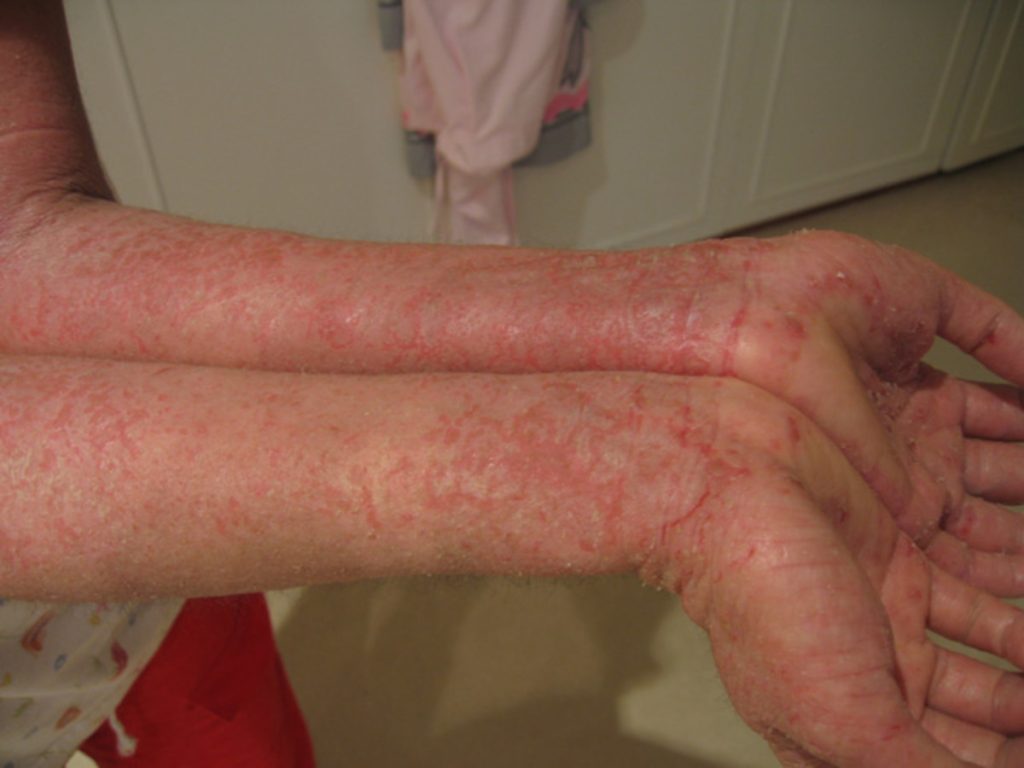
It’s important to note that self-care measures are not a substitute for medical treatment and should be used in conjunction with any prescribed medications. If you suspect you have dyshidrotic eczema, it is important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Is Dyshidrotic Eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema is a type of eczema that affects the skin on the hands and feet. It is characterized by small, itchy blisters that can be painful and cause cracking and peeling of the skin. Symptoms include itchy, scaly skin and small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The exact cause of dyshidrotic eczema is not known, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Causes Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
The exact cause of dyshidrotic eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some possible causes include:
Allergies:
Certain substances such as nickel, cobalt, and chromates found in jewelry, watches, or other metal objects can cause a reaction on the skin.
Stress:
Stress can lead to an increased likelihood of developing dyshidrotic eczema.
Weather:
Hot and humid weather can make symptoms worse.
Hormonal changes:
Dyshidrotic eczema can be more common in women who experience hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause.
Other medical conditions:
Individuals with atopic dermatitis, hay fever, or asthma have a higher risk of developing dyshidrotic eczema.
It’s important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop dyshidrotic eczema and not everyone with dyshidrotic eczema will have these risk factors.
Symptoms Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
The symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema typically appear on the hands and feet and can include:
Itchy, scaly skin:
The skin on the hands and feet may become red, itchy, and scaly.
Small, fluid-filled blisters:
Blisters filled with clear fluid may appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
Cracking and peeling skin:
The skin may crack and peel as the blisters dry out.
Painful skin:
The skin may be painful or tender to the touch.
Swelling:
The affected area may be swollen.
Symptoms can vary in severity and duration, and they may come and go. These symptoms can be accompanied by itching, which may be intense. In some cases, the blisters may become infected if they are scratched or broken open.
It’s important to see a doctor if you are experiencing any of these symptoms as they may suggest dyshidrotic eczema and proper treatment is needed.
Treatment Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Treatment for dyshidrotic eczema typically involves a combination of self-care measures and medications. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and prevent secondary infections.
Self-care measures include:
Keeping the skin moisturized:
Using a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer can help to keep the skin hydrated and reduce itching.
Soaking in warm water:
Soaking the affected areas in warm water can help to soften the skin and reduce itching.
Avoiding irritants:
Avoiding substances that may irritate the skin, such as harsh soaps and detergents, can help to prevent flare-ups.
Medications that may be prescribed include:
Topical corticosteroids:
These medications reduce inflammation and itching. They are applied to the skin as a cream, ointment, or lotion.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors:
These medications also reduce inflammation and itching. They are applied to the skin as a cream or ointment.
Oral antihistamines:
These medications can help to relieve itching.
Oral or topical antibiotics:
These medications are used to treat or prevent secondary infections.
Light therapy (phototherapy) may also be used to treat this condition, it involves exposing the affected skin to UV light under the supervision of a dermatologist.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and to monitor the condition to make sure that the treatment is effective.
Prevention Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Preventing can be difficult, as the exact cause of the condition is not fully understood. However, there are some steps you can take to help reduce your risk of developing this condition or to prevent flare-ups:
Avoid triggers:
If you know what triggers your dyshidrotic eczema, try to avoid those triggers as much as possible. Common triggers include certain metals, soaps, and lotions.
Keep your skin moisturized:
Keeping your skin well-moisturized can help to reduce itching and inflammation. Use a fragrance-free moisturizer and apply it to your skin after bathing or showering.
Take care of your hands and feet:
Make sure to keep your hands and feet clean and dry. Wear comfortable shoes that fit well and avoid tight-fitting shoes.
Manage stress:
Stress can trigger flare-ups of dyshidrotic eczema, so it’s important to find ways to manage stress such as yoga, meditation, or talk therapy.
Identify and avoid potential allergens:
If you suspect that an allergen is causing your eczema, see an allergist for a patch test to identify the allergen.
Avoid extremes of temperature:
Avoid getting your hands and feet too hot or too cold, as this can make symptoms worse.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a prevention plan that is tailored to your specific needs and to monitor the condition to make sure that the prevention strategies are effective.
Dyshidrotic Eczema Treatment At Home
There are several self-care measures that you can take at home to help alleviate the symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema:
Soak in warm water:
Soaking the affected areas in warm water can help to soften the skin and reduce itching. Adding a cup of baking soda to the water can also help to soothe the skin.
Keep the skin cool:
Avoid overheating the skin, as this can make symptoms worse. Keep the affected areas cool with a cool compress or by taking cool baths or showers.
Manage stress:
Stress can trigger flare-ups of dyshidrotic eczema, so it’s important to find ways to manage stress such as yoga, meditation, or talk therapy.
Keep your skin clean:
Keep the affected area clean, dry, and well moisturized.
There are several home remedies that may help to alleviate the symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema. These remedies are not a substitute for medical treatment, but they may help to reduce itching, inflammation, and discomfort.
Moisturize With Aloe vera Gel:
Keep the affected skin well-moisturized with a fragrance-free moisturizer. Applying moisturizer after bathing or showering can help to lock in moisture and reduce itching.
Colloidal oatmeal for dyshidrotic eczema:
Colloidal oatmeal can be added to bathwater or made into a paste and applied to the skin to help reduce itching and inflammation.
Tea tree oil :
Tea tree oil has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties and may help to reduce itching and inflammation when applied topically.
Apple cider vinegar:
Apple cider vinegar has anti-inflammatory properties and can be used as a compress to help soothe irritated skin.
Vitamin E oil For dyshidrotic eczema :
Vitamin E oil is a natural moisturizer that can help to reduce itching and inflammation.
Coconut oil for dyshidrotic eczema :
Coconut oil has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties and can be used as a moisturizer to help soothe irritated skin.
It’s important to note that these home remedies are not suitable for everyone, and it’s always best to test them on a small patch of skin first and to speak to a healthcare professional before trying them. Some of these remedies may cause an allergic reaction or worsen the condition in some individuals.
Conclusion:
Dyshidrotic eczema is a type of eczema that affects the hands and feet, characterized by small, itchy blisters that can be painful and cause cracking and peeling of the skin. The exact cause of dyshidrotic eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors such as allergies, stress, weather, hormonal changes, and other medical conditions.
Treatment options include the use of topical and oral medications, as well as light therapy. Self-care measures such as keeping the skin moisturized, soaking in warm water, avoiding irritants, managing stress, and keeping the skin clean and dry can also help to alleviate symptoms.
Prevention can be difficult as the exact cause is not fully understood, but avoiding triggers, keeping the skin moisturized, taking care of hands and feet, managing stress, identifying and avoiding potential allergens, and avoiding extremes of temperature can help to reduce the risk of developing the condition or prevent flare-ups.
If you are experiencing symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema, it is important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Home remedies may also help to alleviate symptoms, but it’s always best to speak to a healthcare professional before trying them.