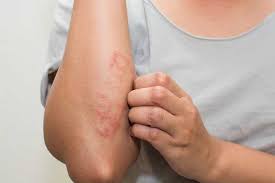
Another name for Atopic dermatitis is atopic eczema. It is the most common worldwide inflammatory skin disease and presents as skin dryness, rash, and itchiness. Atopic Dermatitis vs Eczema: Do you know how they differ? Most people think that eczema and atopic dermatitis are the same, but, they are not. Atopic dermatitis is a common type of eczema.
Scroll till the end to learn, prevention, natural tips, symptoms, and some FAQs about atopic dermatitis.
What Is Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Eczema is a general term for rash-like skin conditions. It causes itchiness often. The skin becomes red and inflamed after scratching. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema that affects 9.6 million children and about 16.5 million adults in the US.
Reduce pigmentation, melasma, and dark spots naturally
Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis
The main symptoms of atopic dermatitis are dry itchy skin that often turns into a rash mostly red in color during flare-ups. It often causes severe itching, especially at night. Patches develop (red, brown, or gray) on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees. In infants, patches develop on the face and scalp.
Is Atopic Dermatitis The Same As Eczema
The short answer is NO. It is difficult to know the right answer about eczema vs atopic dermatitis. Both refer to inflamed and irritated skin, but there are some key differences between the two conditions.
Essential ways to remove pre-mature aging
Atopic Dermatitis VS Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is a type of eczema. Most people use the terms atopic dermatitis and eczema correspondently to refer to conditions that cause dryness, rashes, itchiness, rashes, and other skin lesions. Atopic dermatitis typically begins during childhood. It often causes a red rash in the creases of the elbows and knees. In babies, symptoms develop on the cheeks and scalp.
It can also sometimes be related to a food allergy or it is common among people with a personal or family history of hay fever or asthma. Affected areas of the skin may turn darker in color and scratching makes them infected by developing small bumps.
Other Types Of Eczema
Below are the other types of eczema:
- Asteatotic eczema
- Contact dermatitis
- Discoid or nummular dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic eczema
- Neurodermatitis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Varicose or stasis dermatitis
Natural Tips To Cure Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Use mild cleansers.
- Gently exfoliate the skin.
- Take an oatmeal bath.
- Wear linen, silk, or cotton clothes.
- Get a massage.
- Moisturize skin twice a day.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Apply sunflower oil/coconut oil on the damp skin to “lock in” moisture.
- Put a cool damp cloth on the affected areas in order to ease itching.
- Change your diet. Avoid foods that are mentioned below:
cow’s milk
eggs
soy products
gluten
nuts
fish
shellfish.
Prevention For Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Properly moisturize skin.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid harsh cleansers, soap, detergents, and scented products.
- Do not use harsh exfoliators.
- Use luke-warm water baths.
- Avoid tight clothing.
- Keep nails short.
- Cover affected areas.
When To See A Doctor
If a person notices the following symptoms, he/she should see a doctor:
- Symptoms get worse day by day.
- Itching and pain that affects sleep
- Lesions in new areas
- Fever and chills
- weepy skin with fluid.
- Feeling dull.
Frequent Asked Questions
Q. Will atopic dermatitis ever go away?
A. Symptoms of this type of eczema will come and go, and the tendency for a person to develop these signs may never disappear permanently and completely.
Q. How do you treat atopic dermatitis on the face?
Below are the tips that you can follow to treat eczema on the face:
- Moisturize the face twice a day.
- Cover the affected areas with anti-itch cream.
- Avoid scratching.
- Apply bandages to prevent scratching.
- Take a short lukewarm bath.
- Use organic soap/cleansers (contains no fragrance, chemicals, or preservatives)
- Use a humidifier.
Q. What foods make eczema worse?
A. Below are some main examples of foods that can make eczema worse:
- Citrus fruits.
- Dairy.
- Eggs.
- Gluten or wheat.
- Soy.
- Spices, such as vanilla, cloves, and cinnamon.
- Tomatoes.
- Some nuts.