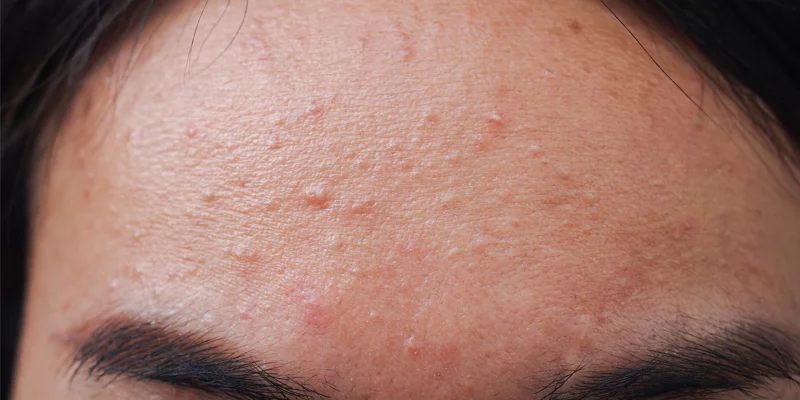
Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or Malassezia folliculitis. Scroll till the end to find out its causes, and symptoms, how to diagnose fungal acne, prevention, treatment and home remedies.
What Is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or Malassezia folliculitis, is a type of skin condition that resembles acne but is caused by an overgrowth of yeast or fungi on the skin. It typically appears as small, itchy, and red bumps on the forehead, chin, and jawline, and may be accompanied by blackheads or whiteheads.
The condition is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, which normally lives on the skin and is not harmful. However, certain factors such as hormonal changes, excessive sweating, and the use of certain skincare products can trigger the yeast to multiply, leading to the development of fungal acne.
Fungal acne is often treated with antifungal medications, such as topical or oral azoles, which work to kill the Malassezia yeast. It is also important to avoid using oily or comedogenic skincare products that can further aggravate the condition. In addition, practicing good hygiene, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and avoiding excessive sweating can also help to prevent fungal acne.
Fungal Acne Causes
Fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast or fungi on the skin, specifically the Malassezia yeast. However, there are several factors that can contribute to the development of this condition, including:
Hormonal changes:
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during puberty or menstrual cycles, can increase the production of sebum (oil) in the skin, creating a favorable environment for Malassezia yeast to thrive.
Excessive sweating:
Sweating can also create a moist environment that promotes the growth of Malassezia yeast.
Certain medications:
Some medications, such as antibiotics or oral contraceptives, can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and yeast on the skin, leading to an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast.
Wearing tight clothing:
Tight clothing can create friction and trap moisture against the skin, which can promote the growth of Malassezia yeast.
Using oily or comedogenic skincare products:
Using skincare products that contain oils or other pore-clogging ingredients can contribute to the development of fungal acne.
Poor hygiene:
Poor hygiene habits, such as infrequent showering or not washing makeup brushes regularly, can lead to the buildup of oil and dead skin cells on the skin, creating an environment that is conducive to fungal acne.
Symptoms Of Fungal Acne
The symptoms of fungal acne may include:
- Small, red bumps on the skin, typically on the forehead, chin, and jawline.
- Itchy or uncomfortable skin.
- Blackheads or whiteheads.
- Clusters of bumps that may be inflamed or tender.
- Pimples or pustules that may contain pus.
- Skin that looks oily or greasy.
- Skin that is more prone to breakouts or blemishes than usual.
- Skin that appears to be more irritated or sensitive than usual.
- Skin that does not respond well to traditional acne treatments.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of fungal acne can be similar to those of other skin conditions, such as regular acne or eczema, so it’s important to get an accurate diagnosis from a dermatologist if you suspect you may have fungal acne.
How Is Fungal Acne Diagnosed?
Fungal acne can be diagnosed by a dermatologist or other healthcare professional through a physical examination of the affected area, as well as a review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. In some cases, a skin culture or biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
During the physical examination, the dermatologist will typically look for the characteristic small, red bumps on the skin, as well as any other signs of inflammation or irritation. The dermatologist may also ask the patient about their skincare routine, any medications they are taking, and any other factors that may be contributing to their symptoms.
In some cases, the dermatologist may use a special tool called a Wood’s lamp, which emits a type of ultraviolet light that can help to highlight any fungal or bacterial infections on the skin.
If the dermatologist suspects that the patient has fungal acne, they may recommend a course of antifungal medication, such as topical or oral azoles, to treat the infection. If the symptoms do not improve or if the diagnosis is uncertain, further testing may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
What’s The Difference Between Fungal Acne And Regular Acne?
Fungal acne and regular acne are two different types of skin conditions that can have similar symptoms, but they have different underlying causes and require different treatments.
Regular acne is caused by the overproduction of sebum (oil) in the skin, which can clog pores and lead to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. This type of acne is typically caused by hormonal fluctuations, stress, or the use of certain skincare or makeup products that can clog pores.
Fungal acne, on the other hand, is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. This yeast is normally present on the skin, but when it overgrows, it can lead to the formation of small, itchy bumps that resemble acne. Fungal acne is often triggered by factors such as hormonal changes, excessive sweating, or the use of oily or comedogenic skincare products.
While the symptoms of fungal acne and regular acne can be similar, there are some key differences.
Fungal acne typically appears as small, itchy, and red bumps on the forehead, chin, and jawline, while regular acne can appear as pimples, blackheads, or whiteheads on various areas of the face, chest, and back. Fungal acne may also be more resistant to traditional acne treatments and may require antifungal medication to effectively treat the underlying fungal infection.
How Is Fungal Acne Treated
This condition is treated using a variety of methods that are aimed at reducing the overgrowth of Malassezia yeast on the skin.
Here are some of the most common treatment options:
Antifungal medications:
Antifungal medications, such as topical or oral azoles, are often used to treat fungal acne. These medications work by reducing the growth of Malassezia yeast and may be used in combination with other topical or oral medications to reduce inflammation and prevent future breakouts.
Adjusting skincare routine:
It’s important to avoid using oily or comedogenic skincare products, as they can contribute to the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. Instead, opt for non-comedogenic or oil-free products, and use a gentle cleanser to remove oil, dirt, and makeup from the skin.
Maintain good hygiene:
Good hygiene is key to preventing the buildup of oil and dead skin cells on the skin, which can contribute to the growth of Malassezia yeast. Be sure to shower regularly, use clean towels and clothing, and wash makeup brushes and other tools frequently.
Avoid sweating:
Sweating can promote the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin, so it’s important to avoid excessive sweating whenever possible. This may mean avoiding strenuous exercise or wearing loose-fitting clothing that allows air to circulate.
Medications:
In some cases, oral or topical antibiotics may be used to treat secondary bacterial infections that can occur with fungal acne.
UV light treatment:
In some cases, a dermatologist may recommend using UV light therapy to treat fungal acne. This treatment involves exposing the skin to UV light, which can kill the Malassezia yeast and reduce inflammation.
It’s important to note that the treatment for fungal acne may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. It’s important to work with a dermatologist to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and concerns.
How To Treat Fungal Acne Naturally At Home
While it’s important to consult with a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment of fungal acne, there are some home remedies that may help to reduce symptoms and prevent future breakouts.
Home Remedies For Fungal Acne
Here are some home remedies:
Tea tree oil:
Tea tree oil is a natural antifungal and antibacterial agent that may help to reduce the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. Dilute tea tree oil with carrier oil, such as jojoba or coconut oil, and apply it to the affected area using a cotton swab.
Apple cider vinegar:
Apple cider vinegar has antifungal properties and can help to balance the pH of the skin, which can reduce the growth of Malassezia yeast. Dilute apple cider vinegar with water and apply it to the affected area using a cotton ball.
Aloe vera:
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that may help to reduce the redness and inflammation associated with fungal acne. Apply aloe vera gel to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with water.
Honey:
Honey has antibacterial and antifungal properties that may help to reduce the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. Apply raw honey to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with water.
Yogurt:
Yogurt contains probiotics that can help to restore the natural balance of bacteria and yeast on the skin. Apply plain, unsweetened yogurt to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with water.
In addition to the home remedies listed above, there are some other things you can do at home to help manage fungal acne:
Use a sulfur-based soap:
Sulfur is a natural antifungal and antibacterial agent that can help to reduce the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. Use a sulfur-based soap to wash the affected area daily.
Use an antifungal cream:
Over-the-counter antifungal creams containing active ingredients like ketoconazole or clotrimazole can help to reduce the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. Apply the cream to the affected area as directed.
Use a benzoyl peroxide cream:
Benzoyl peroxide is a topical medication that can help to reduce acne breakouts, including fungal acne. Use a benzoyl peroxide cream to spot-treat the affected area.
Avoid wearing makeup:
Makeup can contribute to the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin, so it’s important to avoid wearing makeup whenever possible. If you must wear makeup, opt for non-comedogenic products and remove them promptly at the end of the day.
Practice good hygiene:
Practicing good hygiene can help to reduce the risk of developing this. Keep the affected area clean and dry, and avoid touching or picking at the acne lesions.
While these home remedies and tips may provide some relief from fungal acne, it’s important to seek medical treatment if your symptoms persist or worsen. A dermatologist can provide a proper diagnosis and prescribe medications or other treatments as needed.
How Can I Prevent Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne can be prevented by taking certain steps to reduce the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. Here are some tips to prevent this:
Keep skin clean:
One of the most effective ways to prevent this is to keep the skin clean and free from oil, dirt, and dead skin cells. Wash your face twice a day with a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser. Avoid using hot water or harsh scrubs that can irritate the skin.
Avoid oil-based skincare products:
Oil-based skincare products can contribute to the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin, so it’s important to avoid it whenever possible. Opt for non-comedogenic or oil-free products instead.
Moisturize:
While it’s important to avoid oily skincare products, it’s also important to keep the skin moisturized. Use a non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
Avoid sweating:
Sweating can promote the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin, so it’s important to avoid excessive sweating whenever possible. This may mean avoiding strenuous exercise or wearing loose-fitting clothing that allows air to circulate.
Wear breathable clothing:
Wearing breathable clothing made from natural fibers, such as cotton. It can help to reduce the buildup of sweat and oil on the skin, which can contribute to the growth of Malassezia yeast.
Avoid sharing personal items:
Sharing personal items, such as towels, clothing, and makeup brushes can spread bacteria and yeast between individuals. Sharing these can increase the risk of fungal acne. Avoid sharing these items whenever possible.
Seek medical treatment:
If you suspect that you may have fungal acne, it’s important to seek medical treatment from a dermatologist or other healthcare professional. Early treatment can help to prevent the condition from worsening and reduce the risk of scarring or other complications.
By following these tips, you can help to prevent the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin and reduce the risk of developing fungal acne.
Conclusion:
Fungal acne, caused by the overgrowth of Malassezia yeast on the skin, is a common condition that can cause a variety of symptoms, including small bumps, pustules, and redness. While it can be mistaken for regular acne, fungal acne requires different treatment methods. A combination of antifungal medication, topical creams, and good skincare habits can effectively manage fungal acne. It’s important to consult with a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment to avoid potential complications and reduce the risk of future breakouts.