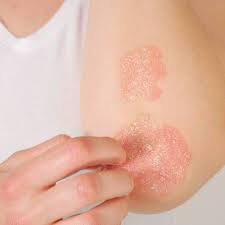
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes patches of thick, red, scaly skin to develop. Read this article till the end to find out the causes, types, symptoms, treatment, home remedies, and some ways to prevent Psoriasis.
What Is Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. It is caused by an overactive immune system, which triggers skin cells to grow too quickly and form patches. The patches often itch or burn, and can be painful. There is no cure, but it can be managed with treatments such as topical creams, light therapy, and medication. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system.
Psoriasis can be treated with a combination of topical medications, light therapy, and oral medications. In severe cases, systemic medications, such as biological drugs, may be used. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
While there is no cure, many people are able to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life with proper treatment.
Types Of Psoriasis
There are several types, including:
Plaque psoriasis:
This is the most common type and is characterized by raised, red, and scaly patches of skin.
Guttate psoriasis:
This type is characterized by small, red, scaly spots that develop on the skin, most commonly on the trunk, legs, and arms.
Inverse psoriasis:
This type is characterized by smooth, red patches of skin that develop in body folds, such as the groin, under the breasts, and in the armpits.
Pustular psoriasis:
This type of psoriasis is characterized by raised, red, and scaly patches of skin that are filled with pus.
Erythrodermic psoriasis:
This type of psoriasis is characterized by widespread redness and itching of the skin and can cause the skin to shed in large sheets.
Nail psoriasis:
This type of psoriasis affects the nails and can cause the nails to become discolored, thick, and brittle.
Scalp psoriasis:
This type of psoriasis affects the scalp and can cause the scalp to become red, scaly, and itchy.
What Causes Psoriasis?
The exact cause of this chronic skin condition is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to an overactive immune system. In people with this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing them to multiply rapidly. This leads to the formation of thick, red, scaly patches on the skin.
Several factors may trigger this condition, including:
Genetics:
There may be a genetic component to this condition, as it tends to run in families.
Environmental triggers:
Certain environmental factors, such as stress, injury to the skin, infections, and exposure to cold weather, can trigger flare-ups.
Medications:
Certain medications, such as lithium and beta-blockers, can trigger or worsen symptoms.
Smoking:
Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of developing this condition, as well as make symptoms worse.
Obesity:
Being overweight or obese has been linked to an increased risk of developing this condition, as well as more severe symptoms.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the specific factors that may be contributing to your symptoms, as well as the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
What Are The Symptoms Of Psoriasis?
The symptoms can vary depending on the type of psoriasis, but common symptoms are below.
Psoriasis Symptoms
Thick, red, scaly patches on the skin:
These patches, also known as plaques, are typically found on the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and face.
Itching and burning sensations:
The skin can become itchy and uncomfortable, especially in severe cases.
Pain and tenderness in the affected areas:
The skin can become painful and tender to the touch, especially in areas where the plaques have become thick and hard.
Stiff and swollen joints (in some cases):
In some cases, psoriasis can also cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, known as psoriatic arthritis.
Nail changes:
Psoriasis can cause changes in the appearance of nails, such as pitting, separation from the nail bed, and thickened nails.
Skin shedding:
In severe cases, large sections of skin can shed, causing patches of raw, red skin to be exposed.
How To Treat Psoriasis
Treatment for this chronic skin condition can vary depending on the severity of symptoms and the type of psoriasis. Common treatments include:
Treatment Of Psoriasis
Topical medications:
Topical creams, ointments, and gels can be applied directly to the skin to help reduce inflammation, slow the growth of skin cells, and relieve itching and burning sensations.
Light therapy:
Also known as phototherapy, light therapy uses ultraviolet (UV) light to slow the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
Oral medications:
In severe cases, oral medications, such as methotrexate or cyclosporine, may be used to slow the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
Biologic drugs:
In severe cases, biological drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, can be used to target specific proteins involved in the immune system that contribute to the symptoms of this condition.
Lifestyle changes:
Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, quitting smoking, and managing stress can also help to improve symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs. In many cases, a combination of treatments may be used to manage symptoms and improve the overall quality of life.
Natural Ways To Treat Psoriasis
In addition to conventional treatments, several home remedies may help to relieve the symptoms and reduce flare-ups:
Aloe vera:
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to soothe the skin and relieve itching and burning sensations.
Oatmeal bath:
An oatmeal bath can help to soothe the skin and relieve itching and burning sensations.
Apple cider vinegar:
Apple cider vinegar has anti-inflammatory properties and can help to balance the skin’s pH, which may help to reduce symptoms.
Coconut oil:
Coconut oil has anti-inflammatory properties and can help to moisturize the skin and reduce itching and burning sensations.
Fish oil:
Fish oil supplements contain omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and may help to improve symptoms.
Dead sea salt:
Dead sea salt contains high levels of minerals, including magnesium, potassium, and calcium, that can help to soothe the skin and reduce itching and burning sensations.
Vitamin D:
Vitamin D can help to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
It’s important to keep in mind that these remedies may not work for everyone and may not be suitable for all types of psoriasis. It’s always best to speak with a healthcare provider before trying any new remedies to ensure that they are safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
Psoriasis Prevention
There is no surefire way to prevent this condition, as the exact cause of this chronic skin condition is not fully understood.
However, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing this condition or minimize the severity of symptoms:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle:
Eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress can help to maintain overall health and reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Avoid triggers:
Identifying and avoiding environmental triggers, such as stress, exposure to cold weather, and certain medications, can help to reduce the risk of developing this condition or minimize the severity of symptoms.
Protect your skin:
Wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen, and avoiding excessive exposure to UV light can help to protect your skin from sun damage, which can trigger or worsen symptoms.
Avoid alcohol:
Consuming alcohol can trigger or worsen symptoms and increase the risk of developing this condition.
Quit smoking:
Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of developing this condition and make symptoms worse.
Treat infections:
Promptly treating infections, such as strep throat, can help to prevent flare-ups and minimize the severity of symptoms.
It’s always best to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best strategies for preventing this condition or managing symptoms, as individual needs and risk factors can vary. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent the development of severe symptoms and improve the overall quality of life.